A Global Perspective on Supercomputer Power Provisioning: Case Studies from United States and Europe
Jun 11, 2025·
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
 ,
,
,
,
·
0 min read
,
,
,
,
·
0 min read
Tapasya Patki
Barry Rountree
Torsten Wilde
Andrea Bartolini
Stephanie Brink
Esa Heiskanen
Sachin Idgunji
Matthias Maiterth
James Rogers
Ermal Rrapaj
Ralf Schneider
Woong Shin
Kathleen Shoga
Christian Simmendinger
Nicholas J Wright
Zhengji Zhao
Abstract
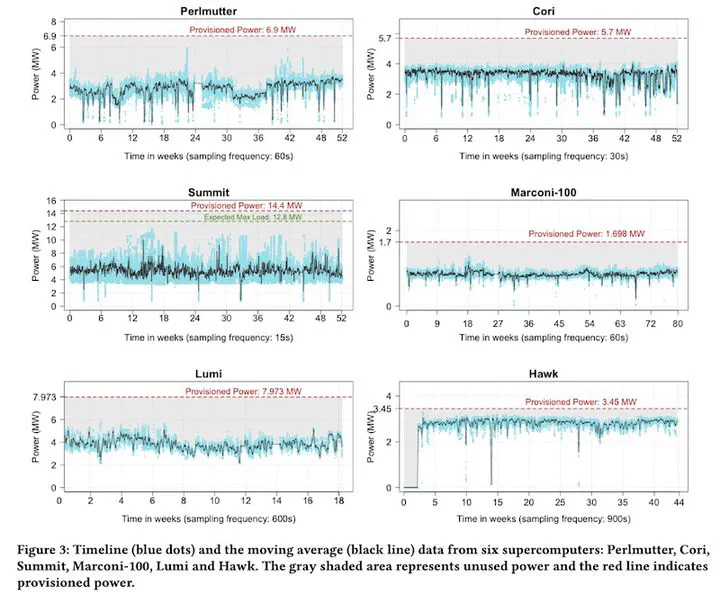
Electrical provisioning in high performance computing is transitioning from simple nameplate Thermal Design Power (TDP) models to more nuanced approaches based on expected electrical load. This paper captures current power provisioning strategies across six international supercomputing centers and seven systems, three of which (Lumi, Summit, Sierra) were in the top 10 of the Top500 list at the time of data collection. We present longitudinal and summary data of actual power consumption as well as a discussion of how each site approached the question of provisioning. We conclude with a discussion on future directions of hardware overprovisioning and its implications for machine and electrical utilization.
Type
Publication
ACM International Conference on Supercomputing 2025